Publication date: September 5, 2025
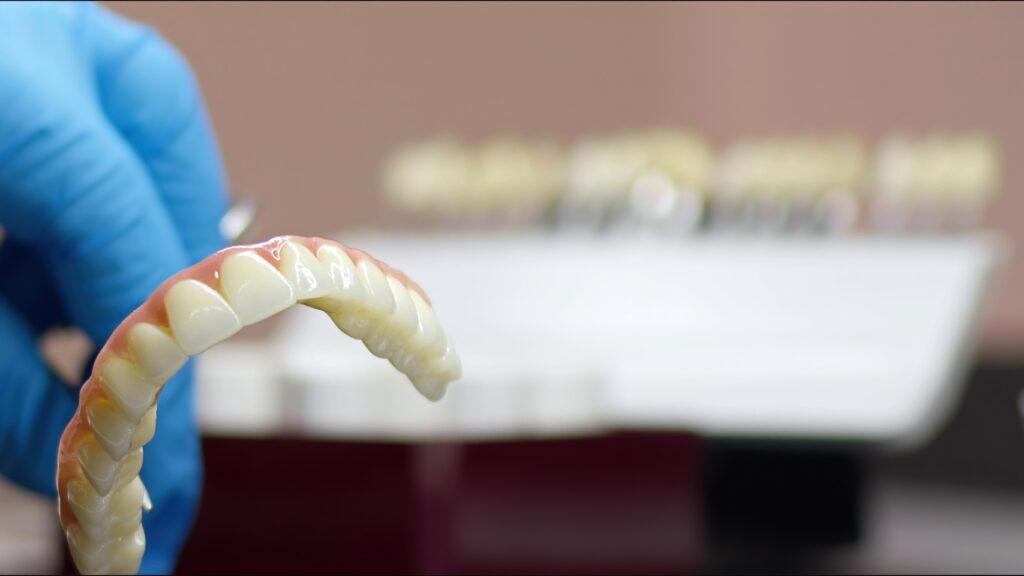
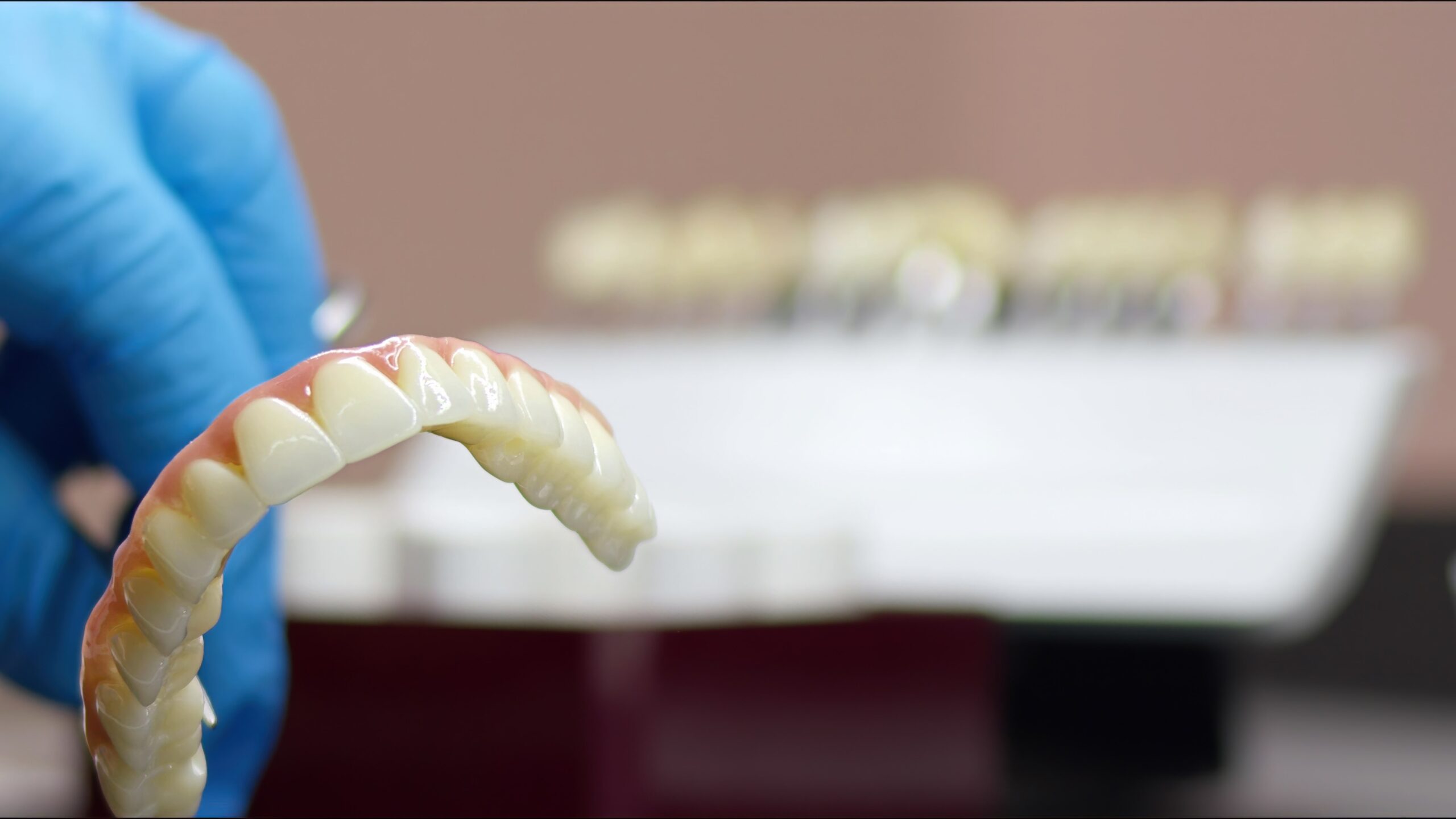
3D printed teeth are a revolutionary product in the world of modern dentistry. The technology is integrated to produce prosthetic dental products, such as bridges, abutments, crowns, and veneers, with exceptional speed and accuracy. Find out how they are helping people achieve transformative levels of oral health.
How Do 3D Printed Teeth Work?
3D printed teeth are created through a process called additive manufacturing. A digital design is created, providing a template for layers of material that can be customized to the patient’s mouth. The print process is as follows:
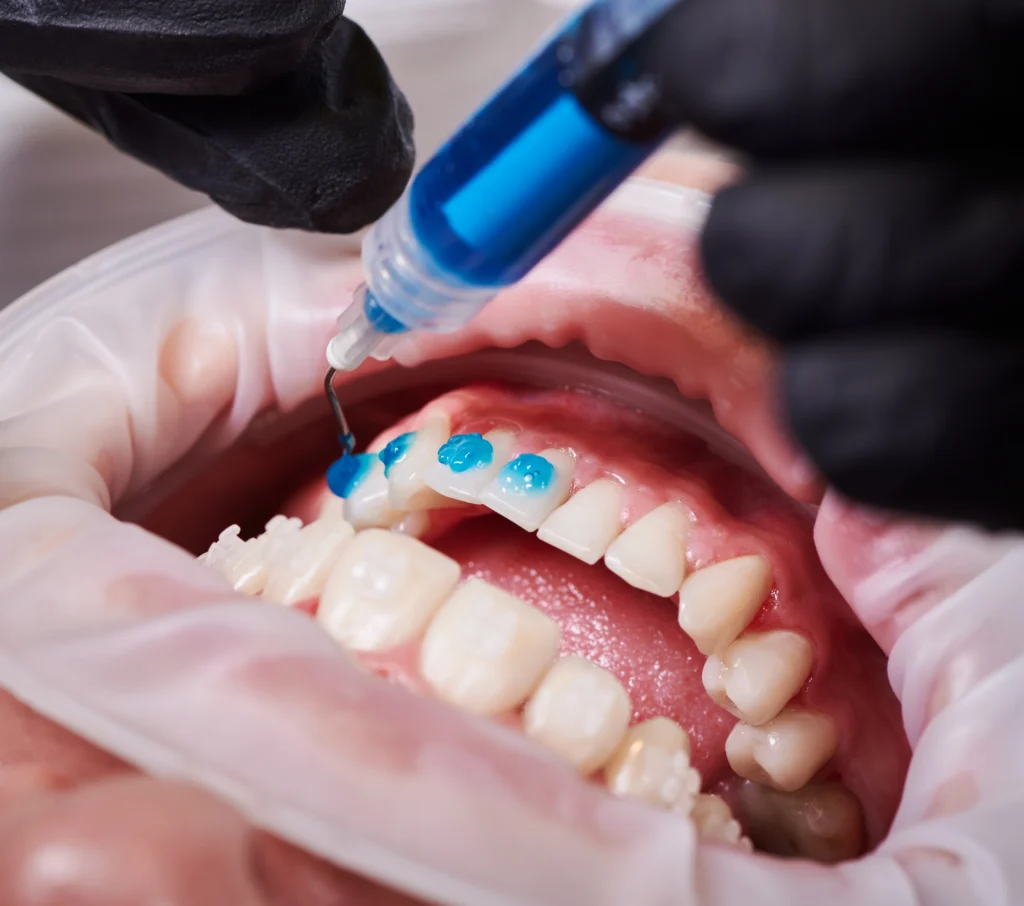
1. The dentist scans the patient’s mouth and creates a 3D model.
2. The model is imported into CAD/CAM software, allowing for precise customization.
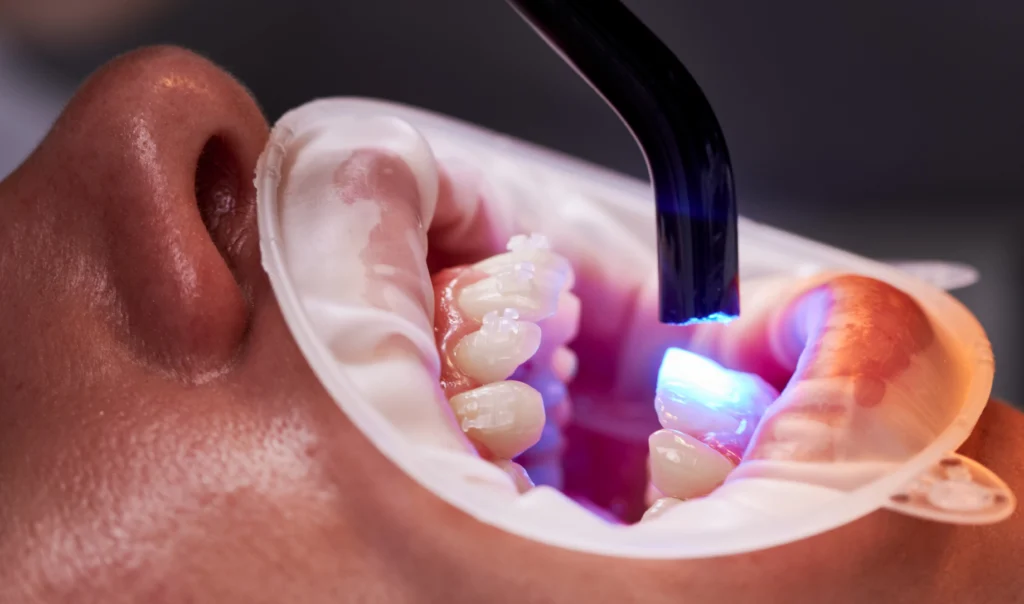
3. The design is sent to a 3D printer, where it undergoes a process in which photopolymer resin is applied layer by layer to create a restoration based on the digital image.
4. After printing is complete, post-processing occurs, which may include curing, polishing, and finishing.
5. The tooth or partial is sent to the provider and fitted in the patient’s mouth.
What are 3D Printed Teeth Used For?
Printed teeth are not dental implants; they are the prosthetic components attached to the implant. Prosthetic examples include:
- Crowns and bridges
- Temporary restorations
- Custom abutments
- Surgical guides
- Diagnostic models
- Dentures
What are the Benefits of 3D Printed Teeth?
The technology offers the following benefits:
- More efficient production leads to shorter wait times for patients and less material waste overall
- Precise techniques lead to improved fit and aesthetics
- More predictable outcomes
- Easier modifications due to the digital approach
- Longer-lasting results due to stronger materials and better processes
Materials Used
Various materials can be used to produce 3D printed teeth, such as:
- Metals
o Titanium and titanium alloys are strong and corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for implants and abutments
o Cobalt chromium, a strong material often used for load-bearing structures
- Ceramics and composites
o Zirconia and other ceramics are strong and have lifelike aesthetics. They are often used in crowns and veneers.
o Resin-based composites provide a combination of moderate strength and lifelike aesthetics.
- Polymers are often used in temporary restorations like aligners and surgical guides because they are lightweight and flexible.
The material choice depends on the patient’s specific needs. However, all material must meet the following requirements:
- Non-toxic
- Non-allergenic
- Has high mechanical and chemical stability over time
- Passes standardized testing
Absolute Smile Provides 3D Printing Technology
Absolute Smile is always at the top of medical technology. We have integrated 3D printing into several procedures, offering our patients fast and effective results. Our updated services allow us to deliver the very best in crowns, bridges, veneers, and implants, while still offering the basics, like checkups and cleanings, that make us a preferred family dentist.
Contact us to schedule your appointment today.
FAQ
How much does a 3D printed denture cost?
Prices vary, but the average cost is $300 to $500 per denture.
What are the disadvantages of 3D printing in dentistry?
3D printing has revolutionized the dental industry, but several limitations remain, primarily based on materials, costs, post-processing requirements, and regulatory concerns. Once these issues are addressed, the technology can advance, and we may soon see a time when it can handle the entire implant process.
How long does it take to 3D print a denture?
A denture can be printed in 1 to 2 hours.
Can you eat with 3D dentures?
Yes, you can eat with 3D dentures. Dentists advise starting with softer foods until you get used to your dentures. However, even when you’re up to speed, you should avoid food that’s extremely hard or chewy.